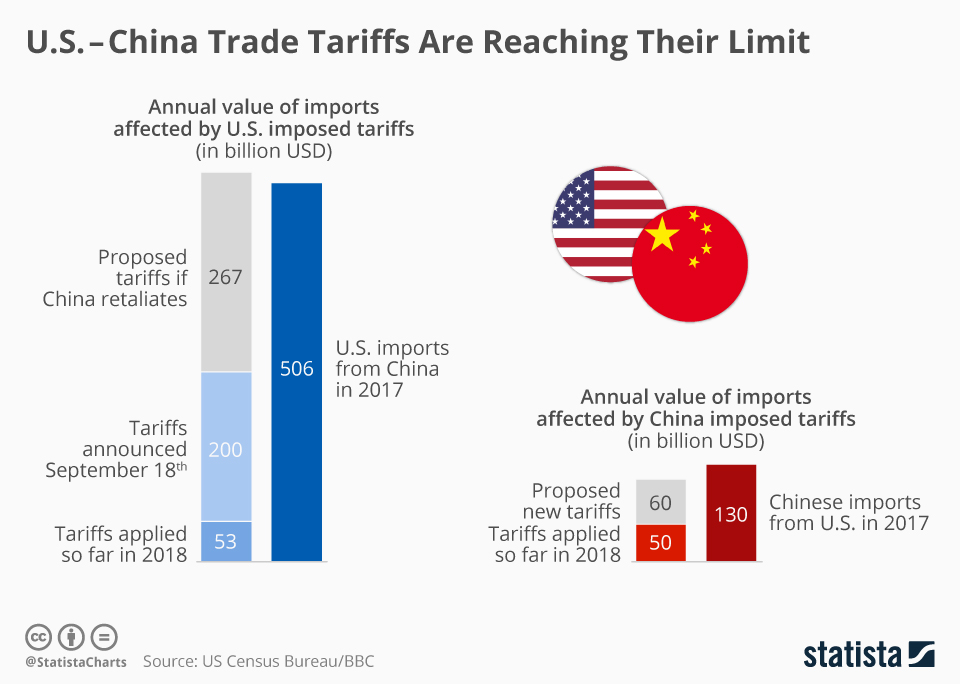
China Tariffs Impact: Economic Consequences for U.S. Allies
The impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy is a multifaceted issue that has significant implications for international trade. As tensions escalate in U.S.-China trade relations, the imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports could lead to rising prices for consumers and disruptions within the global supply chain. Economists fear that such tariffs may not only harm China’s struggling economy but could also rebound negatively on American consumers, burdening them with increased costs. The potential consequences of a renewed trade war extend beyond economics; they can also strain relationships with U.S. allies who may reevaluate their trade ties in light of America’s evolving policies. Amid these complexities, understanding the broader ramifications of tariffs is crucial for predicting the future of transpacific dynamics and stability in global markets.
Examining the repercussions of tariffs imposed on Chinese goods reveals a tangled web of economic relationships that have evolved over decades. As the U.S. considers raising duties on imports from China, the ramifications touch not just the economy but also geopolitical alliances and trade stability. The escalating trade war poses threats to the seamless flow of goods, which many nations have come to rely on for their economic health. In conjunction with emerging markets in Asia and beyond, alternative sourcing options could reshape the landscape of international trade, highlighting the delicate balance that nations must navigate. Ultimately, discerning the consequences of this trade strategy goes beyond mere statistics; it involves understanding how interconnected global economies respond to shifts in trade policies.
Understanding the Impact of U.S.-China Trade Relations
U.S.-China trade relations have been a cornerstone of global economic interactions for decades. The relationship oscillates between cooperation and confrontation, which significantly impacts not only the two countries involved but also the global economy. Recent tariffs imposed by the U.S. on Chinese goods, such as electronics and machinery, reflect an intensified focus on reducing trade deficits and addressing perceived unfair trading practices. Economists argue that the ripple effects of these tariffs extend far beyond the immediate economies involved, affecting global supply chains and market stability.
The deep-rooted interconnectedness between the U.S. and China means that changes in tariffs can lead to significant shifts in consumer prices and product availability. As American consumers face higher prices on imported goods due to tariffs, it creates a cascade of economic challenges—including inflationary pressures and increased costs of production for U.S. manufacturers reliant on Chinese components. This complexity underscores how U.S.-China trade policies profoundly affect the global economic landscape.
The Role of Tariffs on Chinese Imports
The imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports is framed as a strategic maneuver to safeguard American jobs and industries. However, it presents a double-edged sword; while aiming to protect domestic markets, these tariffs can lead to substantial price increases for consumers. Products such as smartphones and household goods, which often rely on components manufactured in China, could see marked inflation as U.S. companies pass on the costs associated with tariffs to their customers. This consumer burden poses questions about the long-term sustainability of such economic policies, raising concerns about their effectiveness in achieving the intended outcomes.
Moreover, the tariffs may inadvertently harm U.S. interests by straining relationships with allies. As China’s economy faces pressures from reduced exports to the U.S., it may seek more robust alliances with other nations, potentially leading to a divided global market. The prospect of higher prices and weakened competitive advantage for U.S. firms raises alarms about the trade war’s consequences, prompting calls for a more nuanced approach to U.S.-China relations rather than one dominated by punitive tariffs.
Global Supply Chain Disruptions and Their Fallout
In an increasingly interconnected world, global supply chain disruptions caused by tariffs can lead to economic instability across multiple nations. With many industries reliant on just-in-time manufacturing processes that utilize components from multiple countries, any increase in tariffs can create bottlenecks that hinder production rates. These disruptions are particularly pronounced in technology sectors where equipment and parts must flow seamlessly between the U.S. and China to meet consumer demands.
As businesses weigh the implications of tariffs on Chinese imports, many are exploring alternatives for sourcing materials. This transition may lead to increased investments in other countries, such as Vietnam or India, which might step in to fill the void. However, these shifts take time and involve significant workforce training and infrastructure development. Consequently, the immediate aftermath of tariff implementations often leads to delays in production and increased consumer prices, further exacerbating supply chain vulnerabilities.
China’s Economic Response to Tariffs
China’s economy, already impacted by internal challenges, faces formidable obstacles from escalating tariffs imposed by the U.S. The uncertainty surrounding tariffs creates a climate of apprehension among Chinese manufacturers reliant on export markets. Many businesses are currently strategizing on how best to navigate shifting demand, considering longer-term impacts on labor markets and production capabilities. A significant concern is whether China’s economy can pivot quickly enough to mitigate the direct effects of tariffs on its export-driven model.
Economists indicate that while the imposition of tariffs may have stunted growth in key sectors, it could also force China into a new phase of strategic planning. Chinese policymakers are reportedly debating the reallocation of resources to enhance domestic consumer markets as a way to counterbalance decreased export opportunities. Such adjustments, however, would require a delicate balancing act to maintain the current level of international commerce while nurturing internal economic growth.
Consequences of a Renewed Trade War
The potential for a renewed trade war raises significant questions about the dynamics of global commerce. A trade war not only threatens U.S.-China economic ties but also risks alienating partner nations that rely on the stability of U.S.-China relations. Many countries in the Asia-Pacific region could feel the repercussions as export markets either shrink or realign. The fear of uncertainty can deter foreign investment, hampering growth opportunities across the board.
Moreover, the prospect of surging prices within the U.S. could trigger political and social unrest. American consumers may rise in opposition to rising costs of daily goods stemming from tariff-related policies. This unrest can further complicate diplomatic relations and create a formidable roadblock for future negotiations aimed at trade reform. Thus, navigating the aftermath of such high-stakes economic conflict becomes crucial for policymakers both in Washington and Beijing.
Potential Benefits for China Amid Tariff Challenges
While tariffs are ostensibly designed to disadvantage China, they may also present the country with unique opportunities. By galvanizing efforts to deepen ties with other global players, China could potentially offset losses incurred from U.S.-China trade tensions. The possibility of forming stronger commercial partnerships with Europe, Southeast Asia, and Africa may help to diversify China’s trade routes and markets as it seeks to overcome the limitations imposed by U.S. tariffs.
Furthermore, analysts suggest that these challenges could fuel China’s domestic innovation and technological advancements. Pressures arising from external tariffs may catalyze a renewed focus on building indigenous supply chains and improving productivity within Chinese firms. Consequently, China’s efforts to bolster its economic standing could paradoxically enhance its resilience against future trade conflicts, allowing it to adapt more fluidly to changing global economic landscapes.
Market Dynamics Post-Tariffs
The dynamics of global markets are inevitably altered following the introduction of tariffs. For instance, U.S. companies may reconsider sourcing strategies, leading to investment in manufacturing capabilities within other emerging markets. While this diversification might mitigate risks associated with reliance on China, such transitions often come with challenges, including quality control and production costs that may not yield immediate benefits. The landscape of producers is likely to shift, but the timeline for establishing new supply chains can be lengthy and complex.
Consequently, industries must navigate a transformed market space with ingenuity and flexibility. Companies that can swiftly adapt to the new realities of tariffs will find a competitive edge, while those clinging to outdated practices may struggle to survive. Factors such as labor costs, production capabilities, and logistical considerations will play crucial roles in shaping the post-tariff landscape of international trade.
Shifts in Consumer Behavior Due to Tariff Policies
Consumer behavior can shift significantly in response to tariff implementations. As prices rise due to increased tariffs on imports, American consumers may become more inclined to seek out domestically produced alternatives, whether due to financial constraints or nationalistic sentiments. Retailers may also adapt their marketing strategies to highlight U.S.-made products as more favorable options in the face of elevated costs for foreign goods.
However, the immediate consequence of heightened consumer prices could deter spending, attractive as local products might be. Inflation resulting from tariffs could suppress discretionary spending, leading to reduced overall economic activity. Balancing consumer expectations with market realities becomes essential for businesses navigating these tumultuous economic waters as they adapt to changing consumer preferences shaped by tariff strategies.
The Future of U.S.-China Economic Relations
Looking toward the future, U.S.-China economic relations remain precarious. As both countries grapple with their trade policies, the potential for cooperative frameworks aimed at addressing shared interests becomes increasingly critical. Policymakers must explore diplomatic channels to foster communication and negotiation, reducing the likelihood of conflict escalation while seeking mutually beneficial solutions to trade matters.
In a landscape marked by tariffs and trade disruptions, the pathway forward will require sustained engagement and adaptability. Countries must prioritize multilateral approaches to trade that recognize the nuances of global supply chains while promoting fair trading practices. The long-standing relationship between the U.S. and China must evolve, addressing the complexities of today’s economic realities, to shape a balanced and equitable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of China tariffs on U.S.-China trade relations?
The imposition of tariffs on Chinese imports significantly alters U.S.-China trade relations by increasing the cost of goods from China, thereby potentially leading to higher prices for American consumers. This strategy may trigger retaliatory tariffs from China and could further deteriorate diplomatic relations between the two nations.
How do tariffs on Chinese imports affect the global supply chain?
Tariffs on Chinese imports disrupt the global supply chain by raising production costs and creating uncertainty for manufacturers reliant on Chinese components. This can lead to delays, increased prices, and a potential shift of manufacturing bases to countries like Vietnam or India, which may struggle to match China’s efficiency and scale.
What are the potential consequences of tariffs on the China economy?
Tariffs can severely impact the China economy by dampening exports, particularly in key sectors like technology. Reduced access to the U.S. market can exacerbate existing economic challenges in China, leading to slower growth and potential job losses in export-driven industries.
How might the U.S. trade war consequences affect American consumers?
The consequences of the trade war, characterized by increased tariffs on Chinese imports, are likely to manifest as higher prices for everyday consumer goods in the U.S. This inflationary pressure may strain household budgets and reduce consumer spending power.
Which countries are likely to benefit from disruptions in Chinese imports due to tariffs?
Countries like Vietnam, Mexico, and India are positioned to benefit from disruptions in Chinese imports to the U.S. as they may attract investment and provide alternative supply chains to meet American demand, though scalability and capabilities remain key challenges.
What role do tariffs play in the evolution of U.S.-China relations?
Tariffs act as a contentious tool in U.S.-China relations, often seen as a means for the U.S. to exert economic pressure on China. The resulting trade tensions can lead to diplomatic fallout and may push China to forge stronger ties with other nations, potentially realigning global trade dynamics.
Could the impact of tariffs on Chinese imports create supply chain disruptions in the U.S.?
Yes, the tariffs on Chinese imports could create significant supply chain disruptions within the U.S., as many American companies depend on components manufactured in China. Such disruptions could lead to delays, increased costs, and the need for companies to seek alternative suppliers, complicating logistical operations.
What long-term effects might U.S. tariffs have on China’s trade policies?
Long-term U.S. tariffs may compel China to reevaluate its trade strategies, potentially driving Beijing to diversify its export markets and strengthen trade relations with non-U.S. allies. This shift could facilitate China’s growth in emerging markets and lessen its dependency on the American economy.
| Key Point | Implication |
|---|---|
| Potential U.S. Tariffs on China | Could lead to a trade war, disrupting supply chains and increasing prices for American consumers. |
| Response from China | China may strengthen ties with other nations, adjusting its trade strategies to mitigate losses. |
| Impact on the Global Economy | Increased tariffs may push China to seek new markets and alternatives to U.S. imports. |
| Concerns Over Economic Uncertainty | Unclear tariff definitions hinder China’s planning, potentially inviting more negotiations. |
| Long-Term Consequences | A shift in trade alliances could favor China, moving it closer to Europe and other allies. |
Summary
The impact of China tariffs is significant and far-reaching. They pose a threat not only to the U.S. economy—through higher consumer prices and supply chain disruptions—but also risk catalyzing a shift in global trade alliances. China’s economic strategy might pivot to strengthen its relations with other nations if new tariffs are imposed, ultimately altering the landscape of international trade for the long term.