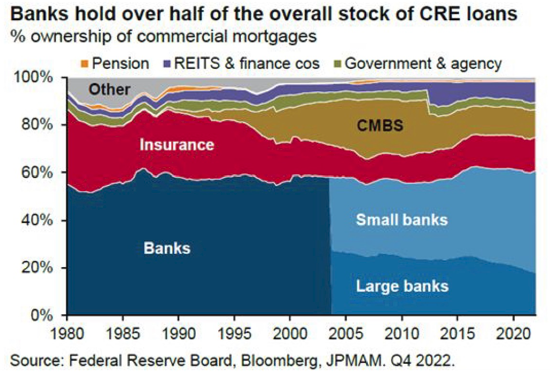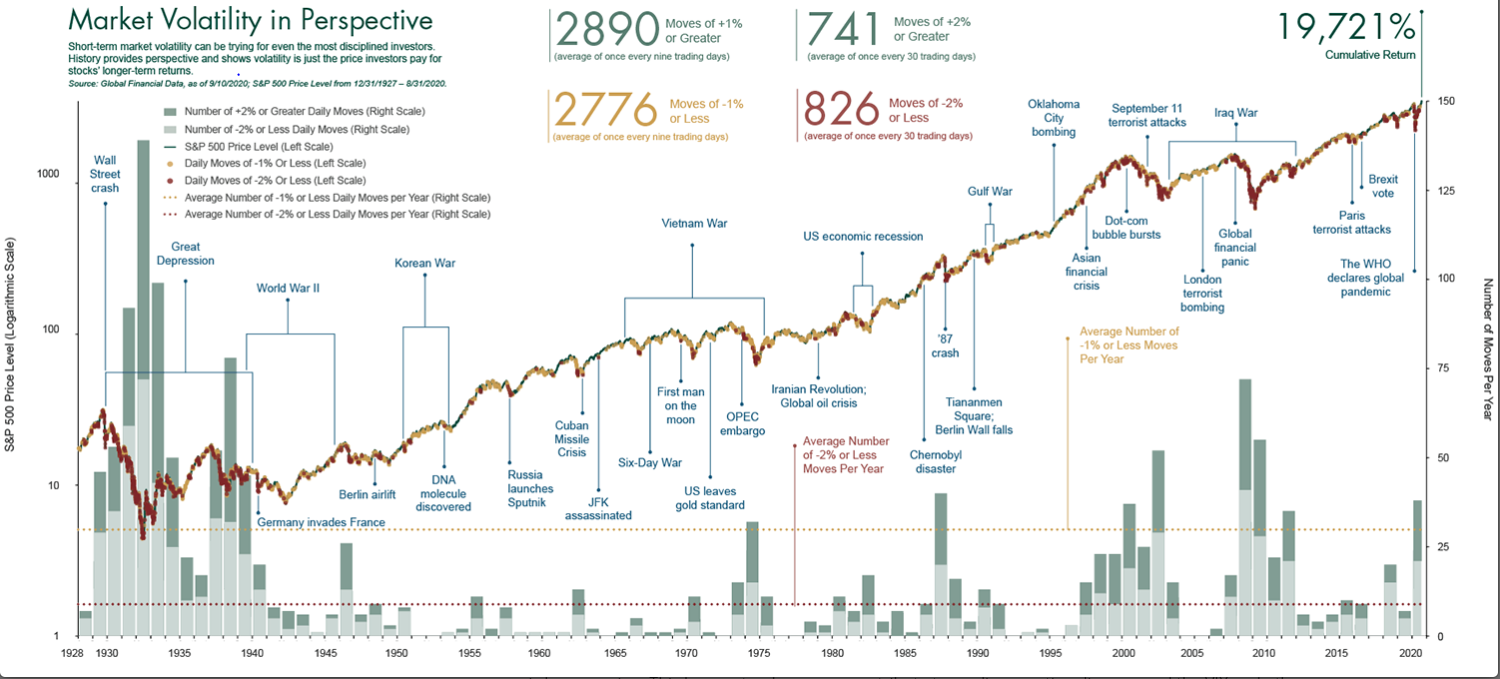
U.S. Economy Recession: Risks from Tariffs and Trade Wars
The U.S. economy recession has become an increasingly pressing concern as market turmoil points to a potential downturn. Recent developments such as escalating tensions in the trade war, falling consumer sentiment indices, and the Federal Reserve’s upcoming decisions on interest rates all contribute to a climate of uncertainty. Investors are particularly wary as tariffs imposed by foreign governments in response to U.S. policies have sparked fears of prolonged economic instability. The complex interplay between these factors raises questions about the impact of tariffs and the overall trajectory of economic growth. As we look ahead, understanding the potential repercussions of these developments on our financial landscape becomes crucial.
As discussions intensify around the looming downturn in the financial system, the phrase “economic contraction” serves as an alternative term to represent what many fear is on the horizon for the United States. Analysts are placing significant emphasis on key indicators such as consumer confidence, the response to international trade policies, and decisions from the Federal Reserve on interest rates. Many predict that the effects of ongoing tariffs could exacerbate existing vulnerabilities within the economy, leading to negative outcomes for production and employment levels. Moreover, the implications for consumer behavior and investment strategies cannot be overlooked, as these are critical to navigating through and out of economic strife. Understanding these dynamics offers a roadmap for assessing potential trends and preparing for both immediate and long-term impacts.
The Current State of the U.S. Economy
The current state of the U.S. economy is marked by increasing volatility and uncertainty, primarily driven by geopolitical tensions and domestic policies. Recent tariff implementations have created a ripple effect across markets, leading to significant declines in stock prices and investor confidence. Economic indicators such as the consumer sentiment index show a downward trend, reflecting the growing apprehension among consumers about the future of the economy. As businesses and households brace for what could be a challenging economic landscape, attention turns toward policy responses from the Federal Reserve.
In this climate of uncertainty, the interplay between trade policies and economic growth has never been more evident. There’s an urgent need to analyze the ongoing effects of tariffs on both domestic production and consumer prices. Experts emphasize that without strategic intervention and cohesive policy frameworks, the risk of falling into a recession looms larger, particularly as global markets react negatively to the U.S.’s trade relations with major partners.
U.S. Economy Recession Predictions
Given the current economic climate, many analysts are voicing concerns about a potential recession on the horizon for the U.S. economy. Factors such as decreasing consumer sentiment, significant losses in the stock market, and the potential for government spending cuts contribute to this apprehension. The warnings from economists highlight a growing awareness that these issues could lead to a contraction in economic activity within the next year. Recessions typically arise not only from poor fiscal management but also from external shocks, making the trade war a critical area of focus.
Research also suggests that the Federal Reserve’s forthcoming decisions regarding interest rates will play a pivotal role in either staving off or accelerating recessionary trends. With inflationary pressures mounting, the challenge lies in managing interest rates without stifling growth. The interplay of these economic realities underscores the fragility of the current state, where one misstep could trigger a downturn, mirroring historical precedents from previous recessions.
Impact of Tariffs on Economic Stability
The imposition of tariffs has significant implications for U.S. economic stability. Economists warn that these trade barriers can disrupt supply chains, inflate consumer prices, and ultimately lead to decreased consumer confidence. The latest reports indicate that businesses are experiencing uncertainty, prompting a shift toward risk-averse strategies as they navigate the complexities imposed by new tariff regulations. This trend reinforces the idea that tariffs may be counterproductive, as they strain both domestic and international trade relationships.
Moreover, the landscape of investor sentiment is notably affected by tariff-related policies, which could deter capital investment and hamper growth. As market reactions suggest, the potential for long-term economic disruption outweighs short-term gains from tariffs. It becomes crucial for policymakers to consider not just the immediate revenue from tariffs, but their broader implications on the economy’s health and growth trajectory.
Consumer Sentiment Index and Economic Outlook
The University of Michigan’s consumer sentiment index, which is at its lowest since late 2022, paints a concerning picture of the American public’s outlook. This measure is a key indicator of economic health, reflecting how consumers feel about job security, inflation, and financial well-being. A decline in consumer confidence often leads to reduced spending, which can further contribute to economic stagnation. As consumers pull back on expenditures, the risk of a recession becomes more pronounced.
Economists stress that a low consumer sentiment index can signal deeper issues within the economy, as spending accounts for a substantial portion of economic growth. If individuals remain hesitant to spend due to economic uncertainty—fueled by trade wars and looming interest rate decisions—the economy could face cascading effects, including rising unemployment and slower recovery rates. Thus, monitoring this index becomes critical for evaluating economic prospects.
Federal Reserve’s Interest Rate Dilemma
The Federal Reserve faces a complex challenge in deciding how to manage interest rates amid economic uncertainty. On one hand, lowering rates could stimulate growth by encouraging borrowing and investments; on the other hand, maintaining higher rates might be necessary to control inflation, particularly in light of recent tariff-induced price hikes. The Fed’s decisions will significantly influence market dynamics and could either mitigate or exacerbate recession risks, making their actions a focal point for economists and policymakers alike.
In times of heightened volatility, the balance the Federal Reserve must strike becomes even more delicate. Trade wars act as adverse supply shocks, complicating the tradeoff between unemployment and inflation. The central bank’s strategies must address these unique challenges, as failure to act decisively could lead to prolonged economic sluggishness and instability. Stakeholders will be keeping a close eye on the Fed’s next moves, as they could shape the economic landscape for years to come.
Trade War Effects on Employment Growth
The ongoing trade war has far-reaching effects on employment growth within the U.S. economy. As companies face increased costs from tariffs, many are forced to reconsider their hiring strategies, leading to a slowdown in job creation. Economists argue that unstable trade environments deter businesses from expanding their workforces, as they grapple with unpredictable costs and demand fluctuations. This stagnation not only hampers individual job seekers but can also have cascading effects on economic growth.
Moreover, reduced hiring can contribute to a decrease in consumer spending power, exacerbating the fears of a recession. With arms-length hiring practices becoming more common, economists warn that long-term unemployment levels could rise, pressuring welfare programs and reducing disposable income. Balanced dialogue between maintaining fair trade practices and safeguarding employment opportunities is essential to navigating these tumultuous economic times.
Risk Perception and Economic Confidence
The current climate of risk perception plays a crucial role in defining the economic trajectory of the U.S. The uncertainty generated by inconsistent government policies, including tariff impositions and spending decisions, has led to increased perceptions of volatility among investors and consumers alike. As confidence falters, the ripple effect can lead to reduced investments and spending, which ultimately impairs economic growth. Economic stability thrives on predictability, and any deviations from that can significantly impact the overall landscape.
Moreover, the effects of heightened risk perception stretch beyond financial markets; they infiltrate consumer behavior and business strategies. Companies may delay investments or hiring due to fears of impending economic downturns, stifling growth opportunities. As the U.S. navigates through this turbulent period, understanding and mitigating these risk perceptions become paramount for fostering an environment conducive to economic recovery.
Evaluating Economic Policy Responses
Evaluating the current economic policy responses is essential to understanding the potential pathways for recovery or further decline. As the Federal Reserve contemplates its next moves, the implications of interest rate adjustments must be weighed carefully against other fiscal measures, including tariff policies. Clarity in economic direction will be critical for stabilizing investor and consumer confidence, which is currently at risk due to erratic policy implementation.
Furthermore, effective communication from policymakers can help alleviate concerns surrounding economic instability. By providing a cohesive vision for economic growth and addressing the multifaceted challenges brought about by tariffs and trade uncertainty, government officials can aim to restore public confidence and encourage active participation in the economy. The evaluative frameworks of past policies will also provide insights into how best to navigate present challenges.
Conclusions on Future Economic Trends
In conclusion, the trajectory of the U.S. economy hinges on several interrelated factors, notably geopolitical tensions, consumer confidence, and policy responses. As predictions regarding a recession become more prevalent, attention must be directed not only towards immediate responses but also long-term strategies that can promote sustainable growth. The lesson here is clear—investors and policymakers must remain vigilant and responsive to the rapidly changing economic landscape.
Looking forward, the ability to adapt and implement effective measures will determine whether the economy can rebound from current adversities. Collaborative efforts between government bodies, industries, and consumers will be essential in overcoming the uncertainties presented by trade wars and inconsistent economic policies. The focus should be not only on surviving the impending recession but on laying the groundwork for future resilience and prosperity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of the U.S. economy in relation to the U.S. economy recession prediction?
As of now, many economists are concerned that the U.S. economy may be heading for a recession within the next year due to several factors, including a trade war, high consumer uncertainty reflected in the consumer sentiment index, and potential cuts in government spending.
How do tariffs impact the U.S. economy and the likelihood of a recession?
The imposition of tariffs has been linked to economic instability and has contributed to negative investor sentiment. As tariffs disrupt trade dynamics, they can lead to increased costs for consumers and businesses, heightening the risk of a recession.
What role does the Federal Reserve play in relation to the U.S. economy recession and interest rates?
The Federal Reserve is faced with the challenge of balancing interest rate cuts to support economic growth while controlling inflation. In uncertain economic conditions, such as those leading toward a recession, the Fed’s decisions on interest rates can significantly influence recovery efforts.
What is the consumer sentiment index, and how does it relate to U.S. economy recession predictions?
The consumer sentiment index measures the overall consumer confidence in the economy. A declining index, as seen recently, often signals increasing concerns among consumers about economic stability, which can be a precursor to recession.
What are the predicted effects of the trade war on the U.S. economy and potential recession risks?
The ongoing trade war has raised fears of a prolonged economic downturn, primarily by increasing uncertainty among investors and consumers. This instability can lead to reduced spending and hiring, both of which are critical for maintaining economic growth.
How can changes in federal policies affect the U.S. economy and recession risk?
Federal policies, particularly those related to tariffs and government spending, directly influence market confidence and economic activity. Erratic policy changes can lead to a slowdown in the economy and escalate the risk of entering a recession.
What historical patterns can indicate a potential recession in the U.S. economy?
Historically, signs such as rising consumer uncertainty, stock market declines, and significant government spending reductions often precede recessions. Current trends suggest that similar patterns may be emerging in the U.S. economy.
Is the current stock market volatility a sign of an impending U.S. economy recession?
Yes, stock market volatility can reflect investor sentiment and expectations for economic performance. If volatility persists, it may heighten recession concerns, as uncertain market conditions typically coincide with diminished economic growth.
How might fiscal crises contribute to a recession in the U.S. economy?
Fiscal crises, such as government shutdowns or downgrades in credit ratings, can create significant economic disruption. Such events often lead to decreased consumer and business confidence, a key factor in recessionary trends.
What are expert opinions on combating potential U.S. economy recession through monetary policy?
Economists debate the best course for mitigating recession risks, with options typically revolving around adjusting interest rates. While some advocate for cuts to stimulate growth, others warn it could exacerbate inflationary pressures, complicating recovery efforts.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Recession Warning | Analysts are concerned about a possible recession due to a trade war and declining consumer confidence. |
| Trade War Impact | Tariffs imposed by China, Mexico, and Canada in response to U.S. policies can aggravate economic conditions. |
| Consumer Sentiment Decline | Consumer sentiment index is at its lowest level since late 2022, indicating reduced economic confidence. |
| Investment Trends | The current tariff policy is causing decreased investor confidence, impacting economic growth negatively. |
| Potential Triggers for Recession | Analysts identify five key factors that could lead to a recession: trade war, stock market crash, cuts in government spending, a fiscal crisis, and increased perception of risk. |
| Federal Reserve’s Dilemma | The Fed faces a challenging decision whether to cut interest rates to stimulate growth or keep them stable to control inflation. |
Summary
The U.S. economy recession is a pressing concern as multiple indicators suggest a downturn is on the horizon. Tariffs and trade wars are creating significant uncertainty, impacting consumer sentiment and investment patterns. As the Federal Reserve contemplates its strategies, the volatility in markets and the potential for job loss add to the fears of a recession, urging a close watch on fiscal policies moving forward.