Housing Affordability Crisis: Understanding the Root Causes
The housing affordability crisis has emerged as one of the most pressing challenges facing Americans today, with skyrocketing home prices pushing homeownership out of reach for many. This crisis, fueled by factors such as stringent land-use regulations and NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies, has stifled construction productivity and hampered housing innovation. Coupled with rising labor and material costs, these housing market challenges have created an environment where affordable housing solutions seem increasingly elusive. As construction firms shrink in size, the decline in innovative practices has only exacerbated the issue, leading to a stagnant market characterized by smaller, bespoke developments rather than efficient, mass-produced homes. Addressing this crisis requires a comprehensive understanding of the economic landscape and a proactive approach to reforming policies that inhibit growth in the housing sector.
The current situation regarding affordable living spaces can be described as a severe housing shortfall, where many individuals and families struggle to find homes within their financial reach. This predicament has been driven by various factors, including restrictive zoning laws and community opposition to new developments, often referred to as NIMBYism. The slowdown in construction productivity and the evident decline in innovation within the housing sector have led to a scenario where the dream of homeownership is slowly fading for a significant portion of the population. Moreover, a trend of increasing costs associated with housing development has created barriers that further complicate any attempts to address these issues. Understanding the dynamics at play is essential for crafting viable solutions to ensure that everyone has a place to call home.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
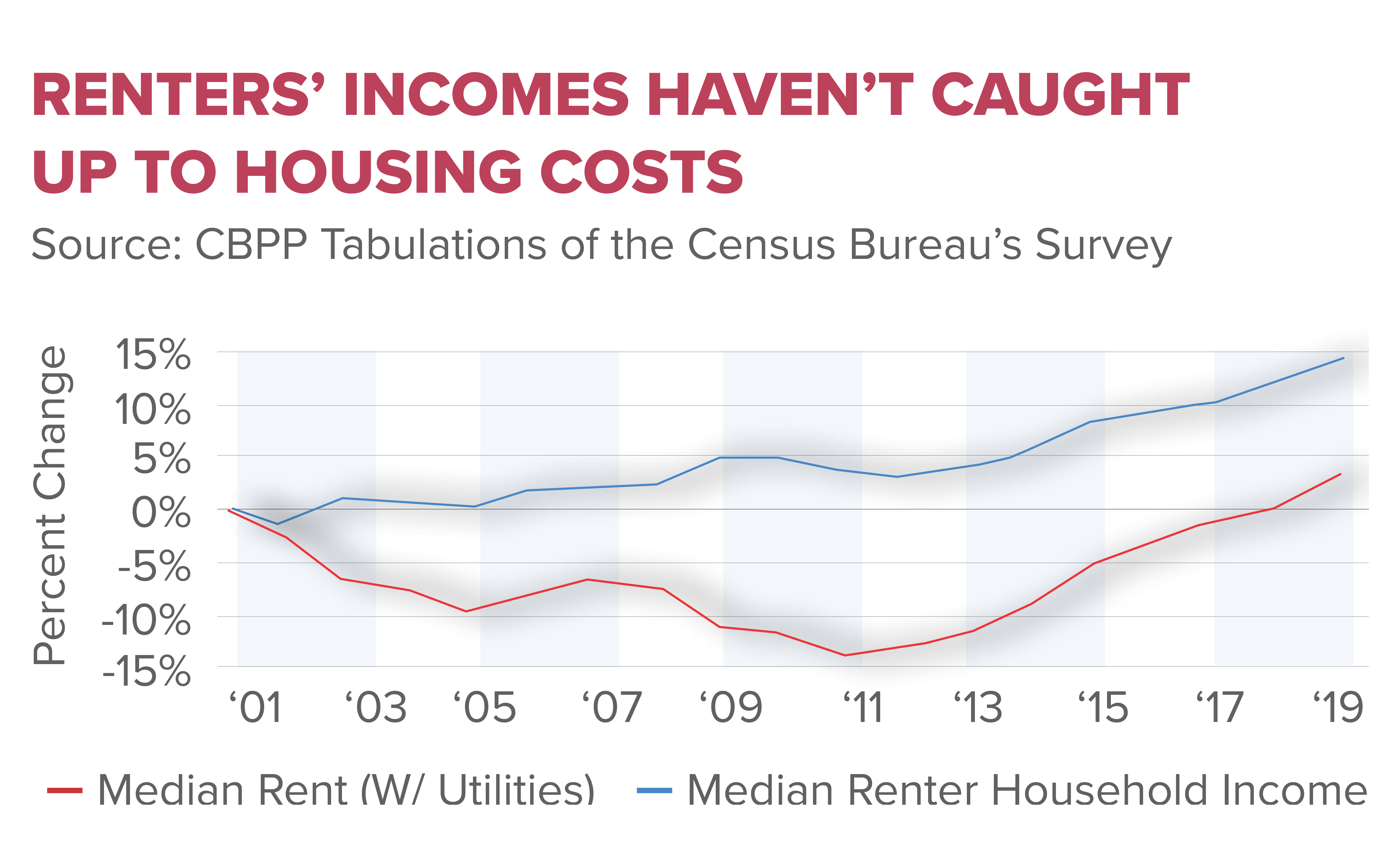
The housing affordability crisis in the United States is a pressing issue affecting millions of families across the nation. Recent studies indicate that the cost of homeownership has soared, rendering it nearly unattainable for a growing segment of the population. Factors influencing this crisis include rising labor and material costs, but new research underscores the significant impact of restrictive land-use regulations. These regulations often stem from the NIMBY (not in my backyard) mentality that hinders large-scale developments, ultimately constraining the housing supply and driving prices higher.
This affordability crisis is exacerbated by a long-term decline in innovation and productivity within the construction sector. Historical data reveals that, while many industries experienced substantial advancements post-1970, construction productivity stagnated as a result of increased regulatory burdens. This shift not only made housing more expensive but also stifled the mass production techniques that had previously made homes affordable. Consequently, younger generations are increasingly finding that homeownership is just beyond their reach, leading to broader economic implications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do land-use regulations contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by imposing restrictions that limit the size and scale of construction projects. These regulations often lead to a decline in construction productivity as builders are forced to focus on smaller, bespoke developments instead of mass-produced homes. Consequently, the costs associated with new housing increases, making ownership out of reach for a growing number of Americans.
What role do NIMBY policies play in the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies exacerbate the housing affordability crisis by creating resistance to new housing developments in local communities. This resistance can manifest as stringent zoning laws and excessive oversight of building projects, which stifle innovation and productivity in construction. As a result, fewer homes are built, driving up prices and reducing access to affordable housing.
Why has housing innovation declined amid the housing affordability crisis?
The housing innovation decline during the housing affordability crisis can be attributed to increased land-use regulations and smaller construction firms, which face less incentive to invest in cost-saving innovations. Historically, large builders benefited from economies of scale, but the rise of restrictive policies has hampered the ability to build larger projects efficiently, diminishing overall innovation in the sector.
What are the housing market challenges contributing to the affordability crisis?
The housing market challenges contributing to the affordability crisis include rising land-use regulations, labor shortages, material cost increases, and decreased construction productivity. These factors combined lead to fewer housing units being produced, which further elevates prices and limits the availability of affordable housing options for many Americans.
How can addressing construction productivity help mitigate the housing affordability crisis?
Improving construction productivity could help mitigate the housing affordability crisis by enabling builders to develop homes more efficiently and at lower costs. Streamlining regulatory processes and encouraging larger-scale projects can foster mass production techniques that replicate the successful housing developments of the mid-20th century, ultimately making homes more affordable and accessible.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| The Housing Affordability Crisis | Home ownership is increasingly out of reach for Americans, with new home prices more than doubling since 1960. |
| Stifling Regulations | Land-use regulations, particularly NIMBY policies, have restricted the ability of builders to create large-scale projects. |
| Declining Construction Productivity | Since 1970, productivity in construction has fallen significantly, contrary to the productivity growth in other industries. |
| Impact of Project Size | Larger projects lead to greater efficiencies; however, current projects are overwhelmingly smaller, affecting costs and innovation. |
| Aging Population and Wealth Transfer | Younger households have seen a decline in home equity compared to older generations, leading to wealth disparities. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis presents a significant challenge for many Americans, with homeownership becoming increasingly unattainable. Key factors contributing to this crisis include restrictive land-use policies and diminishing productivity within the construction sector. Historically, housing construction adapted to mass-production techniques that benefitted consumers with lower prices. However, modern regulations have hindered these advancements, resulting in smaller project scales and stagnation in innovation. Consequently, the younger population faces substantial barriers to owning homes, highlighting the urgent need for reformed policies to improve housing affordability.